코루틴
- Kotlin Serialization, Kotlin Lincheck과 함께 코틀린에서 지원하는 공식 라이브러리로 동시성을 지원하는 라이브러리
- 기존의 쓰레드 기반 비동기 프로그래밍의 복잡성과 성능 한계를 극복하기 위해 설계되었으며, 동시성을 처리하는 강력한 도구
- 비동기 non-blocking으로 동작하는 코드를 동기 방식으로 작성할 수 있도록 지원
- 단, 컴파일된 후의 결과는 동지적으로 동작하지 않음
- CoroutineContext를 통해 Dispatcher, Error Handling, 그리고 ThreadLocal 등을 지원
- CoroutineScope를 통해 Structured Concurrency와 Cancellation 제공
- Flow, Channel 등의 심화 기능 제공
1. kLogger
- 코틀린에서 로깅을 쉽게 사용할 수 있도록 설계된 경량 라이브러리로 복잡한 설정이나 설정 파일 없이 쉽게 설정하고 사용 가능
- 코틀린과 완벽하게 통합되어, 코틀린 언어의 장점을 활용한 간결하고 읽기 쉬운 코드를 작성 가능
2. 동기 스타일 지원
- runBlocking과 suspend 함수를 통해 비동기 non-blocking 코드를 동기 스타일로 변경 가능
- non-blocking 하지만 동기처럼 보이는 코드를 작성 가능하기 때문에 가독성, 디버깅 측면에서 좋음

부연 설명
- runBlocking은 코루틴을 블로킹 방식으로 실행하며 해당 블록 내에서 비동기 작업이 진행되지만, 마치 동기 코드처럼 순차적으로 실행
- asyncOperation1과 asyncOperation2는 suspend 함수로 비동기 작업을 수행하고 해당 함수들은 비동기적으로 실행되지만, runBlocking 스코프 내에서 호출되므로 동기적인 방식으로 처리
3. CoroutineContext
- 코루틴 실행에 필요한 정보를 관리하는 인터페이스
- 코루틴명, CoroutineDispatcher, ThreadLocal, CoroutineExceptionHandler 등을 제공하여 코루틴의 실행 환경을 제어

부연 설명
- launch(context)에서 앞서 정의한 CoroutineContext를 사용해 코루틴을 실행
- Dispatcher는 코루틴이 실행될 쓰레드를 제어
- Dispatchers.Default는 기본 디스패처로, CPU 집약적인 작업에 적합한 쓰레드 풀에서 실행
4. CoroutineScope
- CoroutineScope를 사용하면 코루틴의 생명 주기를 제어할 수 있으며, 코루틴 내에서 발생한 cancel이 자식 코루틴에도 전파 가능
- CoroutineScope 함수를 통해 별도의 CoroutineScope를 생성하고 해당 스코프 내에서는 자식 Coroutine이 모두 완료되고 끝남을 보장
- cancel이 발생할 경우 자식 CoroutineScope로 cancel을 전파
- delay 함수는 cancel이 전파되면 CancellationException을 수행하여 cancel
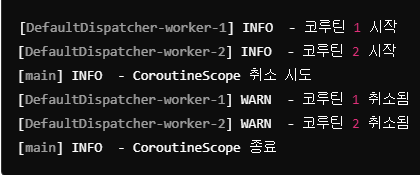
부연 설명
- CoroutineScope(Dispatchers.Default)를 사용하여 새로운 코루틴 스코프를 생성하며 해당 스코프 내에서 실행되는 모든 코루틴은 이 스코프의 생명 주기에 종속됨
- delay(1000L)로 1초를 기다린 후, customScope.cancel()을 호출하여 스코프를 취소하며 이때 스코프 내에서 실행 중인 모든 자식 코루틴(코루틴 1, 코루틴 2)에 취소가 전파
- 스코프가 취소되면, 자식 코루틴에서 CancellationException이 발생하여 try-catch에서 이를 처리
5. Flow
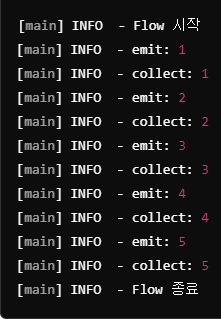
- 코틀린은 Reactor의 Flux와 비슷한 Flow를 제공하여 비동기 스트림을 다룰 수 있는 기능을 제공
- Flow는 데이터를 하나씩 비동기적으로 방출(emit)하고, 구독자는 데이터를 차례대로 수집(collect)할 수 있음
- Reactor의 onNext와 같이 emit을 통해 값을 전달
- Reactor의 subscribe와 같이 collect를 이용하여 item 전달
- flux와 마찬가지로 다양한 연산 제공
- map, flatMap, take와 같은 중간 연산자 제공
- collect, toList, toSet과 같은 종료 연산자 제공
6. Channel
- 채널은 코루틴 간 안전하게 데이터를 주고받을 수 있는 통신 메커니즘이며 여러 코루틴이나 쓰레드에서도 안전성을 보장
- 채널은 비동기적으로 데이터를 송수신할 수 있으며, 기본적으로는 파이프와 같은 역할 수행
- capacity와 BufferOverflow 인자를 설정하여 버퍼의 크기와 동작 방식을 조정 가능
- capacity를 통해 채널의 버퍼 크기 설정
- BufferOverflow 버퍼가 가득 찼을 때의 동작 정의

참고
패스트 캠퍼스 - Spring Webflux 완전 정복 : 코루틴부터 리액티브 MSA 프로젝트까지
반응형
'Kotlin' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Kotlin] CoroutineScope (0) | 2024.10.03 |
|---|---|
| [Kotlin] CoroutineContext (0) | 2024.10.03 |
| [Kotlin] 코루틴 (Coroutine) 기초 (0) | 2024.10.02 |
| [Kotlin] lateinit과 by lazy의 차이점 (2) | 2022.07.13 |