1. suspend 함수
- 코틀린 코루틴에서 비동기적으로 실행할 수 있는 특수한 함수로
- 코루틴 내에서 중단 가능(suspension) 한 작업을 처리할 수 있도록 설계됨
- 실행 일시 중단 가능
- 나중에 다시 실행 재개할 수 있는 특징 지님
- 코루틴 내에서 네트워크 요청이나 파일 읽기/쓰기와 같이 특정 작업을 대기해야 할 때 CPU 리소스를 낭비하지 않고, 효율적으로 다른 작업 처리 가능
1.1 suspend 함수 특징
- 코루틴 내에서만 실행 가능: suspend 함수는 오직 코루틴 내에서만 호출될 수 있으며 코루틴 범위 밖에서는 직접 호출 불가
- 중단 및 재개 가능: 앞서 언급했다시피 suspend 함수는 중간에 실행을 멈추고, 나중에 다시 이어서 실행 가능
- 비동기 작업 처리: suspend 함수는 일반 함수와 달리 비동기 작업을 처리할 수 있으며 이는 시간이 오래 걸리는 I/O 작업에 매우 적합
1.2 suspend 함수 vs 일반 함수
| 특징 | suspend 함수 | 일반 함수 |
| 실행 방식 | 비동기 중단 및 재개 가능 |
동기 호출이 완료될 때까지 대기 |
| 실행 스코프 | 코루틴 내에서만 호출 가능 | 코루틴 외부에서 호출 가능 |
| CPU 점유 | 작업이 완료될 때까지 중단하고 다른 작업 실행 가능 | 작업 중 CPU를 계속 점유 |
| blocking 여부 | 호출 쓰레드를 블로킹하지 않음 non-blocking |
호출 쓰레드를 블로킹 blocking |
1.3 코틀린 코드를 자바 코드로 변환한 뒤 차이점 확인
- Intellij에서 코틀린 코드를 bytecode로 변환한 뒤 Decompile을 통해 bytecode를 자바 코드로 변환 가능
1.3.1 코틀린 코드
- 코틀린 코루틴과 Reactor의 Mono를 함께 사용하는 간단한 예제로 코틀린의 suspend 함수와 Reactor의 비동기 스트림 API를 결합하여 비동기적으로 데이터를 처리하는 방식
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| class SuspendExample { | |
| suspend fun greet(who: String): String { | |
| delay(100) | |
| return getResult(who).awaitSingle() | |
| } | |
| private fun getResult(who: String): Mono<String> { | |
| return Mono.just("Hello, $who!") | |
| } | |
| } |
1.3.2 변환된 자바 코드
- greet 메서드에 Continuation이라는 인자가 추가된 것을 확인 가능
- ContinuationImpl에는 label과 result가 포함되었고
- switch 문을 통해 label에 따라서 코드가 수행되는 것을 확인 가능
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| @Metadata( | |
| mv = {1, 8, 0}, | |
| k = 1, | |
| xi = 48, | |
| d1 = {"\u0000\u0018\n\u0002\u0018\u0002\n\u0002\u0010\u0000\n\u0002\b\u0002\n\u0002\u0018\u0002\n\u0002\u0010\u000e\n\u0002\b\u0004\u0018\u00002\u00020\u0001B\u0005¢\u0006\u0002\u0010\u0002J\u0016\u0010\u0003\u001a\b\u0012\u0004\u0012\u00020\u00050\u00042\u0006\u0010\u0006\u001a\u00020\u0005H\u0002J\u0016\u0010\u0007\u001a\u00020\u00052\u0006\u0010\u0006\u001a\u00020\u0005H\u0086@¢\u0006\u0002\u0010\b¨\u0006\t"}, | |
| d2 = {"Lcom/grizz/wooman/coroutine/basic/SuspendExample;", "", "()V", "getResult", "Lreactor/core/publisher/Mono;", "", "who", "greet", "(Ljava/lang/String;Lkotlin/coroutines/Continuation;)Ljava/lang/Object;", "kotlin-coroutine"} | |
| ) | |
| public final class SuspendExample { | |
| @Nullable | |
| public final Object greet(@NotNull String who, @NotNull Continuation $completion) { | |
| Object $continuation; | |
| label27: { | |
| if ($completion instanceof <undefinedtype>) { | |
| $continuation = (<undefinedtype>)$completion; | |
| if ((((<undefinedtype>)$continuation).label & Integer.MIN_VALUE) != 0) { | |
| ((<undefinedtype>)$continuation).label -= Integer.MIN_VALUE; | |
| break label27; | |
| } | |
| } | |
| $continuation = new ContinuationImpl($completion) { | |
| Object L$0; | |
| Object L$1; | |
| // $FF: synthetic field | |
| Object result; | |
| int label; | |
| @Nullable | |
| public final Object invokeSuspend(@NotNull Object $result) { | |
| this.result = $result; | |
| this.label |= Integer.MIN_VALUE; | |
| return SuspendExample.this.greet((String)null, (Continuation)this); | |
| } | |
| }; | |
| } | |
| Object $result = ((<undefinedtype>)$continuation).result; | |
| Object var5 = IntrinsicsKt.getCOROUTINE_SUSPENDED(); | |
| Object var10000; | |
| switch (((<undefinedtype>)$continuation).label) { | |
| case 0: | |
| ResultKt.throwOnFailure($result); | |
| ((<undefinedtype>)$continuation).L$0 = this; | |
| ((<undefinedtype>)$continuation).L$1 = who; | |
| ((<undefinedtype>)$continuation).label = 1; | |
| if (DelayKt.delay(100L, (Continuation)$continuation) == var5) { | |
| return var5; | |
| } | |
| break; | |
| case 1: | |
| who = (String)((<undefinedtype>)$continuation).L$1; | |
| this = (SuspendExample)((<undefinedtype>)$continuation).L$0; | |
| ResultKt.throwOnFailure($result); | |
| break; | |
| case 2: | |
| ResultKt.throwOnFailure($result); | |
| var10000 = $result; | |
| return var10000; | |
| default: | |
| throw new IllegalStateException("call to 'resume' before 'invoke' with coroutine"); | |
| } | |
| Mono var6 = this.getResult(who); | |
| ((<undefinedtype>)$continuation).L$0 = null; | |
| ((<undefinedtype>)$continuation).L$1 = null; | |
| ((<undefinedtype>)$continuation).label = 2; | |
| var10000 = MonoKt.awaitSingle(var6, (Continuation)$continuation); | |
| if (var10000 == var5) { | |
| return var5; | |
| } else { | |
| return var10000; | |
| } | |
| } | |
| private final Mono getResult(String who) { | |
| Mono var2 = Mono.just("Hello, " + who + '!'); | |
| Intrinsics.checkNotNullExpressionValue(var2, "just(\"Hello, $who!\")"); | |
| return var2; | |
| } | |
| } |
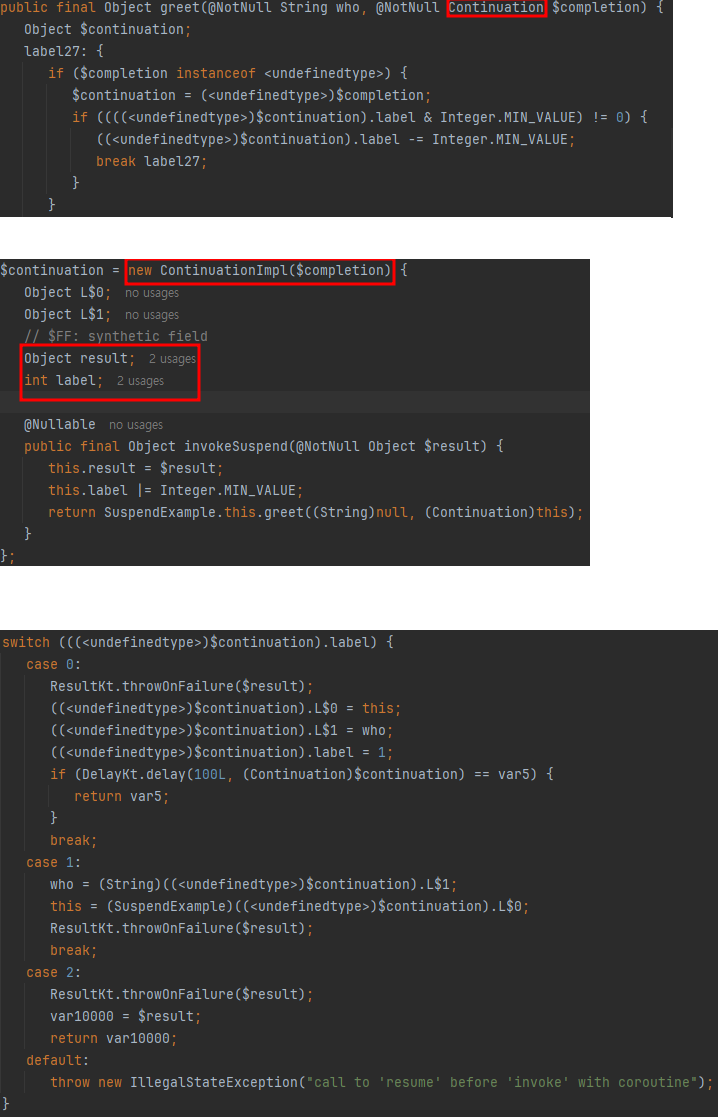
1.3.3 코틀린 코드에서 자바 코드로 변환 결과
- Continuation 인자 추가 및 Continuation 구현체 생성
- switch문 추가
- DelayKt.delay를 호출하며 Continuation 전달하고 종료
- System.out.println 수행
- Unit 반환
* 코틀린 컴파일러가 suspend 함수를 변환하는 과정을 파악하기 위해서는 FSM(Finite State Machine)과 Continuation Passing Style에 대한 이해 필요
2. Finite State Machine
- 유한한 개수의 상태를 갖는 state machine으로 한 번에 오직 하나의 상태만을 가질 수 있음
- 이벤트를 통해 하나의 상태에서 다른 상태로 전환 가능
- 프로그래밍에서는 복잡한 제어 흐름을 관리하기 위해 FSM을 사용
2.1 FSM 구현 방법
- label을 이용해서 when 문을 수행
- 각각의 case에 작업을 수행하고 label을 변경
- 재귀함수를 호출하며 다음 label을 전달하여 상태 변경
- label을 직접 인자로 넘기는 대신 Shared라는 data class를 통해 전달
- 추가로 Shared 내 result 인자에 계산된 결과를 저장하여 재귀함수에 전달
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| // 상태 및 결과를 공유하는 data class | |
| data class Shared( | |
| var label: Int = 0, | |
| var result: Int = 0, | |
| ) | |
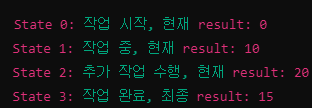
| fun fsm(shared: Shared) { | |
| when (shared.label) { | |
| 0 -> { | |
| println("State 0: 작업 시작, 현재 result: ${shared.result}") | |
| shared.result += 10 | |
| shared.label = 1 | |
| fsm(shared) | |
| } | |
| 1 -> { | |
| println("State 1: 작업 중, 현재 result: ${shared.result}") | |
| shared.result *= 2 | |
| shared.label = 2 | |
| fsm(shared) | |
| } | |
| 2 -> { | |
| println("State 2: 추가 작업 수행, 현재 result: ${shared.result}") | |
| shared.result -= 5 | |
| shared.label = 3 | |
| fsm(shared) | |
| } | |
| 3 -> { | |
| println("State 3: 작업 완료, 최종 result: ${shared.result}") | |
| // 종료 상태이므로 더 이상 재귀 호출하지 않음 | |
| } | |
| else -> { | |
| println("알 수 없는 상태: ${shared.label}") | |
| } | |
| } | |
| } | |
| fun main() { | |
| fsm(shared) | |
| } |
3. Continuation Passing Style
- 함수의 실행이 끝난 후 무엇을 할지에 대한 정보를 Continuation이라는 추가 인자로 전달하는 스타일
- 함수가 직접 결과를 반환하는 대신, 결과를 다음으로 처리할 함수에 넘겨주는 방식
- 값을 반환하는 대신 Continuation을 실행
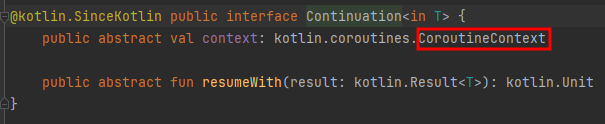
3.1 Continuation 인터페이스
- 코틀린 코루틴에서 Continuation 인터페이스 제공
- resumeWith를 구현하여 외부에서 해당 Continuation을 실행할 수 있는 엔드 포인트 제공
- 이를 위해 CoroutineContext 포함
3.2 Continuation vs Callback
| 특징 | Continuation | Callback |
| 사용 방식 | suspend 함수에서 사용 코루틴의 중단과 재개에 쓰임 |
함수 호출 시 콜백 함수를 전달하여 작업 완료 시 호출 |
| context 유지 | 함수 상태를 유지하고 중단된 지점에서 재개 가능 | 함수 상태 유지 X 완료되면 콜백 호출 |
| 가독성 | 비동기 코드를 동기식 코드처럼 간결하게 작성 가능 | 콜백 함수가 중첩되면 복잡도 올라감 |
| 비동기 코드 흐름 | 중단점에서 재개 | 작업 완료 시점에서 콜백 호출 |
| 예외 처리 | try-catch로 처리 가능 코루틴에서 자체 지원 |
콜백 내부에서 에러 처리를 명시적으로 처리 |
3.3 FSM에 CPS를 적용한 예제
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| import kotlin.coroutines.* | |
| data class State(val label: Int, val result: Int) | |
| fun fsmCps(state: State, continuation: Continuation<State>) { | |
| when (state.label) { | |
| 0 -> { | |
| println("State 0: 작업 시작, 현재 result: ${state.result}") | |
| continuation.resumeWith(Result.success(State(1, state.result + 10))) | |
| } | |
| 1 -> { | |
| println("State 1: 작업 중, 현재 result: ${state.result}") | |
| continuation.resumeWith(Result.success(State(2, state.result * 2))) | |
| } | |
| 2 -> { | |
| println("State 2: 추가 작업 수행, 현재 result: ${state.result}") | |
| continuation.resumeWith(Result.success(State(3, state.result - 5))) | |
| } | |
| 3 -> { | |
| println("State 3: 작업 완료, 최종 result: ${state.result}") | |
| } | |
| else -> { | |
| println("알 수 없는 상태: ${state.label}") | |
| } | |
| } | |
| } | |
| suspend fun fsmCpsSuspend(state: State): State = suspendCoroutine { continuation -> | |
| fsmCps(state, continuation) | |
| } | |
| suspend fun runFSM() { | |
| var state = State(0, 0) | |
| while (state.label != 3) { | |
| state = fsmCpsSuspend(state) // suspend 함수로 상태 전환 | |
| } | |
| } | |
| fun main() = runBlocking { | |
| runFSM() | |
| } |
4. 동기 코드를 코루틴으로 전환하는 과정 예시
4.1 동기 코드
- 고객, 상품, 스토어, 그리고 주소 정보 조회 후 주문을 넣는 mock 코드
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| private val log = kLogger() | |
| class OrderBlockingExample( | |
| private val customerService: CustomerBlockingService, | |
| private val productService: ProductBlockingService, | |
| private val storeService: StoreBlockingService, | |
| private val deliveryAddressService: DeliveryAddressBlockingService, | |
| private val orderService: OrderBlockingService, | |
| ) { | |
| fun execute(userId: Long, productIds: List<Long>): Order { | |
| // 1. 고객 정보 조회 | |
| val customer = customerService.findCustomerById(userId) | |
| // 2. 상품 정보 조회 | |
| val products = productService | |
| .findAllProductsByIds(productIds) | |
| // 3. 스토어 조회 | |
| val storeIds = products.map { it.storeId } | |
| val stores = storeService.findStoresByIds(storeIds) | |
| // 4. 주소 조회 | |
| val daIds = customer.deliveryAddressIds | |
| val deliveryAddress = deliveryAddressService | |
| .findDeliveryAddresses(daIds) | |
| .first() | |
| // 5. 주문 생성 | |
| val order = orderService.createOrder( | |
| customer, products, deliveryAddress, stores | |
| ) | |
| return order | |
| } | |
| } | |
| fun main(args: Array<String>) { | |
| val customerService = CustomerBlockingService() | |
| val productService = ProductBlockingService() | |
| val storeService = StoreBlockingService() | |
| val deliveryAddressService = DeliveryAddressBlockingService() | |
| val orderService = OrderBlockingService() | |
| val example = OrderBlockingExample( | |
| customerService = customerService, | |
| productService = productService, | |
| storeService = storeService, | |
| deliveryAddressService = deliveryAddressService, | |
| orderService = orderService, | |
| ) | |
| val order = example.execute(1, listOf(1, 2, 3)) | |
| log.info("order: {}", order) | |
| } |
4.2 비동기 코드로 전환
- CompletableFuture, Reactive Streams, 그리고 Flow 등을 이용하여 비동기 코드로 전환
- 하지만 비동기 코드로 전환함에 따라 가독성이 떨어짐
- 아도겐 코드와 같은 형태가 되어 코드 복잡도 올라감
- 동기 코드에 비해 가독성이 떨어짐

4.3 비동기 코드에 FSM 적용
- data 클래스인 Shared 객체 정의
- main에서 최초로 실행하는 경우 null이 전달되기 때문에 Shared 객체 생성
- shared의 label 값에 따라 다른 case문을 실행하며 case 문 내에서는 label을 변경하고 이전에 실행됐던 결과를 shared 내부의 중간값에 저장
- 각 case 문마다 cont.result에 값을 저장 후 재귀 호출
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| private val log = kLogger() | |
| class OrderAsyncExampleUpgrade1( | |
| private val customerService: CustomerFutureService, | |
| private val productService: ProductRxjava3Service, | |
| private val storeService: StoreMutinyService, | |
| private val deliveryAddressService: DeliveryAddressPublisherService, | |
| private val orderService: OrderReactorService, | |
| ) { | |
| class Shared { | |
| var result: Any? = null | |
| var label = 0 | |
| // variables | |
| lateinit var customer: Customer | |
| lateinit var products: List<Product> | |
| lateinit var stores: List<Store> | |
| lateinit var deliveryAddress: DeliveryAddress | |
| } | |
| fun execute(userId: Long, | |
| productIds: List<Long>, | |
| shared: Shared? = null) { | |
| val cont = shared ?: Shared() | |
| when (cont.label) { | |
| 0 -> { | |
| // 1. 고객 정보 조회 | |
| cont.label = 1 | |
| customerService.findCustomerFuture(userId) | |
| .thenAccept { customer -> | |
| cont.result = customer | |
| execute(userId, productIds, cont) | |
| } | |
| } | |
| 1 -> { | |
| // 2. 상품 정보 조회 | |
| cont.customer = cont.result as Customer | |
| cont.label = 2 | |
| productService.findAllProductsFlowable(productIds) | |
| .toList() | |
| .subscribe { products -> | |
| cont.result = products | |
| execute(userId, productIds, cont) | |
| } | |
| } | |
| 2 -> { | |
| // 3. 스토어 조회 | |
| cont.products = cont.result as List<Product> | |
| cont.label = 3 | |
| val products = cont.products | |
| val storeIds = products.map { it.storeId } | |
| storeService.findStoresMutli(storeIds) | |
| .collect().asList() | |
| .subscribe() | |
| .with { stores -> | |
| cont.result = stores | |
| execute(userId, productIds, cont) | |
| } | |
| } | |
| 3 -> { | |
| // 4. 주소 조회 | |
| cont.stores = cont.result as List<Store> | |
| cont.label = 4 | |
| val customer = cont.customer | |
| val daIds = customer.deliveryAddressIds | |
| deliveryAddressService.findDeliveryAddressesPublisher(daIds) | |
| .subscribe(FirstFinder { deliveryAddress -> | |
| cont.result = deliveryAddress | |
| execute(userId, productIds, cont) | |
| }) | |
| } | |
| 4 -> { | |
| // 5. 주문 생성 | |
| cont.deliveryAddress = cont.result as DeliveryAddress | |
| cont.label = 5 | |
| val customer = cont.customer | |
| val products = cont.products | |
| val deliveryAddress = cont.deliveryAddress | |
| val stores = cont.stores | |
| orderService.createOrderMono( | |
| customer, products, deliveryAddress, stores, | |
| ).subscribe { order -> | |
| cont.result = order | |
| execute(userId, productIds, cont) | |
| } | |
| } | |
| 5 -> { | |
| val order = cont.result as Order | |
| log.info("order: $order") | |
| } | |
| } | |
| } | |
| } | |
| fun main(args: Array<String>) { | |
| val customerService = CustomerFutureService() | |
| val productService = ProductRxjava3Service() | |
| val storeService = StoreMutinyService() | |
| val deliveryAddressService = DeliveryAddressPublisherService() | |
| val orderService = OrderReactorService() | |
| val example = OrderAsyncExampleUpgrade1( | |
| customerService = customerService, | |
| productService = productService, | |
| storeService = storeService, | |
| deliveryAddressService = deliveryAddressService, | |
| orderService = orderService, | |
| ) | |
| example.execute(1, listOf(1, 2, 3)); | |
| } |
4.3.1 FSM만 적용했을 때의 문제점
- cont.result에 값을 넣고 재귀 함수를 호출하는 코드가 반복됨
- 재귀 함수를 직접 호출하기 때문에 코드를 외부로 분리하기 힘듦
- main 함수에서는 Shared 객체를 생성하지 않기 때문에 결과를 출력하는 부분을 하드 코딩
- 개선하기 위해서는 Continuation을 전달하는 형태로 변경해야 함
4.4 비동기 코드에 CPS 적용
- Shared 객체를 CustomContinuation 객체로 변경
- CustomContinuation은 main으로부터 Continuation을 받음
- 중간값들 뿐만 아니라 매개변수들과 인스턴스까지 Continuation에 저장
- 가장 마지막 state에서 complete를 호출하여 Completion 호출
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| private val log = kLogger() | |
| class OrderAsyncExampleUpgrade2( | |
| private val customerService: CustomerFutureService, | |
| private val productService: ProductRxjava3Service, | |
| private val storeService: StoreMutinyService, | |
| private val deliveryAddressService: DeliveryAddressPublisherService, | |
| private val orderService: OrderReactorService, | |
| ) { | |
| private class CustomContinuation( | |
| private val completion: Continuation<Any>, | |
| ) : Continuation<Any> { | |
| var result: Any? = null | |
| var label = 0 | |
| // arguments and instance | |
| lateinit var that: OrderAsyncExampleUpgrade2 | |
| var userId by Delegates.notNull<Long>() | |
| lateinit var productIds: List<Long> | |
| // variables | |
| lateinit var customer: Customer | |
| lateinit var products: List<Product> | |
| lateinit var stores: List<Store> | |
| lateinit var deliveryAddress: DeliveryAddress | |
| override val context: CoroutineContext | |
| get() = completion.context | |
| override fun resumeWith(result: Result<Any>) { | |
| this.result = result.getOrThrow() | |
| that.execute(0, emptyList(), this) | |
| } | |
| fun complete(value: Any) { | |
| completion.resume(value) | |
| } | |
| } | |
| fun execute(userId: Long, | |
| productIds: List<Long>, | |
| continuation: Continuation<Any>) { | |
| val cont = if (continuation is CustomContinuation) { | |
| continuation | |
| } else { | |
| CustomContinuation(continuation).apply { | |
| that = this@OrderAsyncExampleUpgrade2 | |
| this.userId = userId | |
| this.productIds = productIds | |
| } | |
| } | |
| when (cont.label) { | |
| 0 -> { | |
| // 1. 고객 정보 조회 | |
| cont.label = 1 | |
| customerService.findCustomerFuture(cont.userId) | |
| .thenAccept(cont::resume) | |
| } | |
| 1 -> { | |
| // 2. 상품 정보 조회 | |
| cont.customer = cont.result as Customer | |
| cont.label = 2 | |
| productService.findAllProductsFlowable(cont.productIds) | |
| .toList() | |
| .subscribe(cont::resume) | |
| } | |
| 2 -> { | |
| // 3. 스토어 조회 | |
| cont.products = cont.result as List<Product> | |
| cont.label = 3 | |
| val products = cont.products | |
| val storeIds = products.map { it.storeId } | |
| storeService.findStoresMutli(storeIds) | |
| .collect().asList() | |
| .subscribe() | |
| .with(cont::resume) | |
| } | |
| 3 -> { | |
| // 4. 주소 조회 | |
| cont.stores = cont.result as List<Store> | |
| cont.label = 4 | |
| val customer = cont.customer | |
| val daIds = customer.deliveryAddressIds | |
| deliveryAddressService.findDeliveryAddressesPublisher(daIds) | |
| .subscribe(FirstFinder(cont::resume)) | |
| } | |
| 4 -> { | |
| // 5. 주문 생성 | |
| cont.deliveryAddress = cont.result as DeliveryAddress | |
| cont.label = 5 | |
| val customer = cont.customer | |
| val products = cont.products | |
| val deliveryAddress = cont.deliveryAddress | |
| val stores = cont.stores | |
| orderService.createOrderMono( | |
| customer, products, deliveryAddress, stores, | |
| ).subscribe(cont::resume) | |
| } | |
| 5 -> { | |
| val order = cont.result as Order | |
| cont.complete(order) | |
| } | |
| } | |
| } | |
| } | |
| fun main(args: Array<String>) { | |
| val customerService = CustomerFutureService() | |
| val productService = ProductRxjava3Service() | |
| val storeService = StoreMutinyService() | |
| val deliveryAddressService = DeliveryAddressPublisherService() | |
| val orderService = OrderReactorService() | |
| val example = OrderAsyncExampleUpgrade2( | |
| customerService = customerService, | |
| productService = productService, | |
| storeService = storeService, | |
| deliveryAddressService = deliveryAddressService, | |
| orderService = orderService, | |
| ) | |
| val cont = Continuation<Any>(EmptyCoroutineContext) { | |
| log.info("result: $it") | |
| } | |
| example.execute(1, listOf(1, 2, 3), cont) | |
| Thread.sleep(5000) | |
| } |
* 여전히 재귀 함수를 호출하는 코드가 반복됨
4.5 비동기 코드에서 재귀 함수 반복 호출 제거
- subscribe, thenAccept 후 cont::resume을 넘기는 부분을 Continuation을 인자로 받는 확장 함수로 분리 가능
- 분리할 경우 CompletableFuture, Flowable을 사용할 때는 더 이상 직접 subscribe, thenAccept 등을 사용하지 않더라도 확장 함수를 통해 재귀 함수 반복을 피할 수 있음
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| private val log = kLogger() | |
| class OrderAsyncExampleUpgrade3( | |
| private val customerService: CustomerFutureService, | |
| private val productService: ProductRxjava3Service, | |
| private val storeService: StoreMutinyService, | |
| private val deliveryAddressService: DeliveryAddressPublisherService, | |
| private val orderService: OrderReactorService, | |
| ) { | |
| private class CustomContinuation( | |
| private val completion: Continuation<Any>, | |
| ) : Continuation<Any> { | |
| var result: Any? = null | |
| var label = 0 | |
| // arguments and instance | |
| lateinit var that: OrderAsyncExampleUpgrade3 | |
| var userId by Delegates.notNull<Long>() | |
| lateinit var productIds: List<Long> | |
| // variables | |
| lateinit var customer: Customer | |
| lateinit var products: List<Product> | |
| lateinit var stores: List<Store> | |
| lateinit var deliveryAddress: DeliveryAddress | |
| override val context: CoroutineContext | |
| get() = completion.context | |
| override fun resumeWith(result: Result<Any>) { | |
| this.result = result.getOrThrow() | |
| that.execute(0, emptyList(), this) | |
| } | |
| fun complete(value: Any) { | |
| completion.resume(value) | |
| } | |
| } | |
| fun execute(userId: Long, | |
| productIds: List<Long>, | |
| continuation: Continuation<Any>) { | |
| val cont = if (continuation is CustomContinuation) { | |
| continuation | |
| } else { | |
| CustomContinuation(continuation).apply { | |
| that = this@OrderAsyncExampleUpgrade3 | |
| this.userId = userId | |
| this.productIds = productIds | |
| } | |
| } | |
| when (cont.label) { | |
| 0 -> { | |
| // 1. 고객 정보 조회 | |
| cont.label = 1 | |
| customerService.findCustomerFuture(cont.userId) | |
| .await(cont) | |
| } | |
| 1 -> { | |
| // 2. 상품 정보 조회 | |
| cont.customer = cont.result as Customer | |
| cont.label = 2 | |
| productService.findAllProductsFlowable(cont.productIds) | |
| .toList().await(cont) | |
| } | |
| 2 -> { | |
| // 3. 스토어 조회 | |
| cont.products = cont.result as List<Product> | |
| cont.label = 3 | |
| val products = cont.products | |
| val storeIds = products.map { it.storeId } | |
| storeService.findStoresMutli(storeIds) | |
| .collect().asList().awaitSuspending(cont) | |
| } | |
| 3 -> { | |
| // 4. 주소 조회 | |
| cont.stores = cont.result as List<Store> | |
| cont.label = 4 | |
| val customer = cont.customer | |
| val daIds = customer.deliveryAddressIds | |
| deliveryAddressService.findDeliveryAddressesPublisher(daIds) | |
| .awaitFirst(cont) | |
| } | |
| 4 -> { | |
| // 5. 주문 생성 | |
| cont.deliveryAddress = cont.result as DeliveryAddress | |
| cont.label = 5 | |
| val customer = cont.customer | |
| val products = cont.products | |
| val deliveryAddress = cont.deliveryAddress | |
| val stores = cont.stores | |
| orderService.createOrderMono( | |
| customer, products, deliveryAddress, stores, | |
| ).awaitSingle(cont) | |
| } | |
| 5 -> { | |
| val order = cont.result as Order | |
| cont.complete(order) | |
| } | |
| } | |
| } | |
| private fun <T> CompletableFuture<T>.await( | |
| cont: Continuation<T> | |
| ) { | |
| this.thenAccept(cont::resume) | |
| } | |
| private fun <T> Single<T>.await(cont: Continuation<T>) | |
| where T : Any { | |
| this.subscribe(cont::resume) | |
| } | |
| private fun <T> Uni<T>.awaitSuspending(cont: Continuation<T>) { | |
| this.subscribe().with(cont::resume) | |
| } | |
| private fun <T> Publisher<T>.awaitFirst( | |
| cont: Continuation<T> | |
| ) { | |
| this.subscribe(FirstFinder(cont::resume)) | |
| } | |
| private fun <T> Mono<T>.awaitSingle( | |
| cont: Continuation<T> | |
| ) { | |
| this.subscribe(cont::resume) | |
| } | |
| } | |
| fun main(args: Array<String>) { | |
| val customerService = CustomerFutureService() | |
| val productService = ProductRxjava3Service() | |
| val storeService = StoreMutinyService() | |
| val deliveryAddressService = DeliveryAddressPublisherService() | |
| val orderService = OrderReactorService() | |
| val example = OrderAsyncExampleUpgrade3( | |
| customerService = customerService, | |
| productService = productService, | |
| storeService = storeService, | |
| deliveryAddressService = deliveryAddressService, | |
| orderService = orderService, | |
| ) | |
| val cont = Continuation<Any>(EmptyCoroutineContext) { | |
| log.info("result: $it") | |
| } | |
| example.execute(1, listOf(1, 2, 3), cont) | |
| Thread.sleep(5000) | |
| } |
4.6 코루틴 적용
- 코틀린 컴파일러가 하는 일을 역순으로 수행함으로써 FSM, CPS이 적용된 비동기 코드를 코루틴 코드로 전환
- 코루틴을 사용하면 비동기 영역에서 결과가 반환될 때까지 일시 중단하고 결과가 반환되면 재개 가능 (suspendable)
- 이처럼 코드를 일시 중단하고 재개 가능한 단위를 코루틴이라고 지칭
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
| private val log = kLogger() | |
| class OrderCoroutineExample( | |
| private val customerService: CustomerFutureService, | |
| private val productService: ProductRxjava3Service, | |
| private val storeService: StoreMutinyService, | |
| private val deliveryAddressService: DeliveryAddressPublisherService, | |
| private val orderService: OrderReactorService, | |
| ) { | |
| suspend fun execute(userId: Long, productIds: List<Long>): Order { | |
| // 1. 고객 정보 조회 | |
| val customer = customerService.findCustomerFuture(userId) | |
| .await() | |
| // 2. 상품 정보 조회 | |
| val products = productService | |
| .findAllProductsFlowable(productIds) | |
| .toList().await() | |
| // 3. 스토어 조회 | |
| val storeIds = products.map { it.storeId } | |
| val stores = storeService.findStoresMutli(storeIds) | |
| .collect().asList().awaitSuspending() | |
| // 4. 주소 조회 | |
| val daIds = customer.deliveryAddressIds | |
| val deliveryAddress = deliveryAddressService | |
| .findDeliveryAddressesPublisher(daIds) | |
| .awaitFirst() | |
| // 5. 주문 생성 | |
| val order = orderService.createOrderMono( | |
| customer, products, deliveryAddress, stores, | |
| ).awaitSingle() | |
| return order | |
| } | |
| } | |
| suspend fun main(args: Array<String>) { | |
| val customerService = CustomerFutureService() | |
| val productService = ProductRxjava3Service() | |
| val storeService = StoreMutinyService() | |
| val deliveryAddressService = DeliveryAddressPublisherService() | |
| val orderService = OrderReactorService() | |
| val example = OrderCoroutineExample( | |
| customerService = customerService, | |
| productService = productService, | |
| storeService = storeService, | |
| deliveryAddressService = deliveryAddressService, | |
| orderService = orderService, | |
| ) | |
| example.execute(1, listOf(1, 2, 3)); | |
| } |
부연 설명
- 코틀린 컴파일러는 suspend가 붙은 함수에 Continuation 인자 추가
- 다른 suspend 함수를 실행할 경우 소유하고 있는 Continuation 전달
- 이러한 변환으로 인해 앞서 언급했다시피 suspend가 없는 함수는 전달할 Continuation이 없기 때문에 다른 suspend 함수 호출 불가
- suspend 함수 내부를 when 문을 이용해서 FSM 상태로 변경
- 각각의 state에서는 label을 변경하고 비동기 함수를 수행
- 비동기 함수가 완료되면 continuation.resume을 수행하여 다시 복귀하지만 label이 변경되면서 다른 state로 전환
- 마지막 state에 도달하면 completion.resume을 수행하고 종료
5. Spring WebFlux에서 코루틴 적용
- 앞서 언급했다시피 suspend 함수는 suspend 함수나 코루틴 내부가 아니라면 실행 불가
- 하지만 Spring WebFlux는 다음과 같은 케이스에 대해서도 suspend 함수를 호출할 수 있도록 지원
- Controller 내부에서 suspend 함수를 호출해야 하는 케이스
- 변경 불가능한 interface가 Mono나 CompletableFuture 등을 반환하고 suspend 함수가 아닌 케이스
5.1 Spring WebFlux suspend 함수 지원
- Spring WebFlux는 suspend 함수 지원
- Context1, MonoCoroutine, Dispatchers.Unconfined를 context로 갖고 reactor-http-nio-2 쓰레드에서 실행

- RequestMappingHandlerAdapter가 handlerMethod를 실행하고 handlerMethod로부터 invocableMethod를 획득하고 invoke를 통해 실행
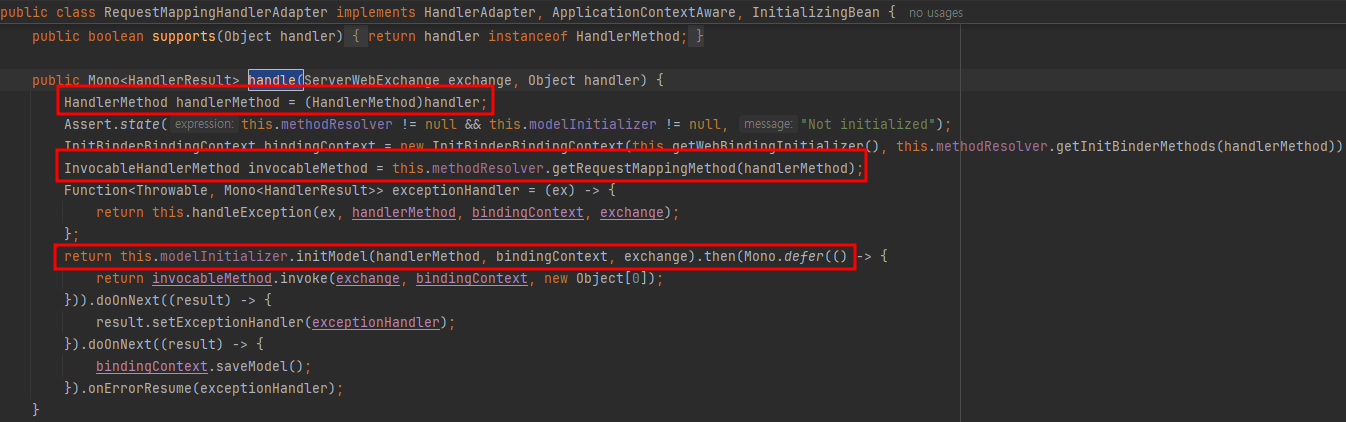
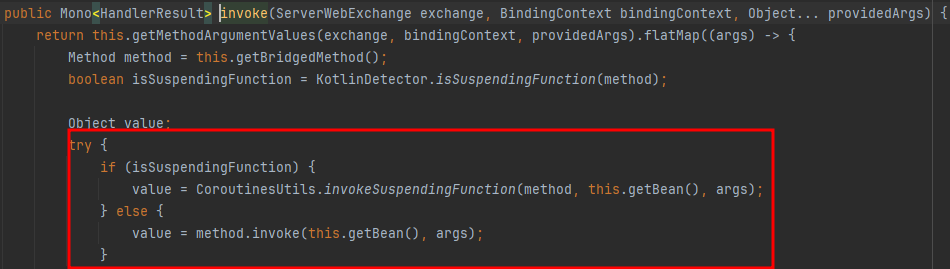
- 주어진 메서드가 suspend 함수인지 체크하고 suspend 함수가 맞다면 CoroutineUtils.invokeSuspendingFunction을 실행하고 아니라면 method.invoke 실행
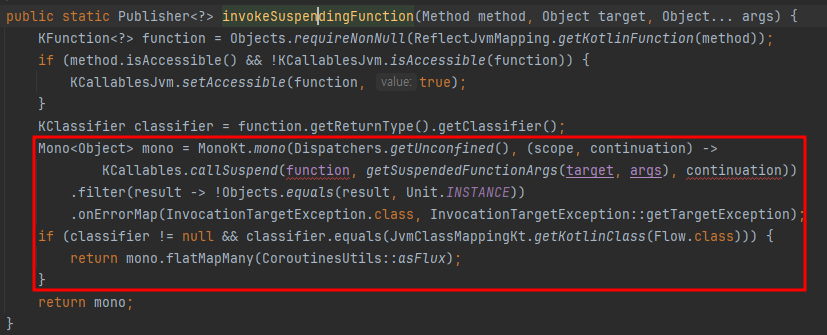
- invokeSuspendingFunction 내부에서 mono를 실행하며 Dispatchers.Unconfined를 전달
- Flow를 반환한다면 mono.flatMapMany를 사용
5.2 외부 라이브러리에서 제공되는 인터페이스가 Mono를 반환하는 경우 suspend 함수 호출하는 방법
- kotlin-coroutines-reactor에서 mono 함수를 제공
- mono 함수를 이용해서 내부에서 suspend 함수 실행
- mono 함수의 결과값은 Mono이기 때문에 그대로 반환
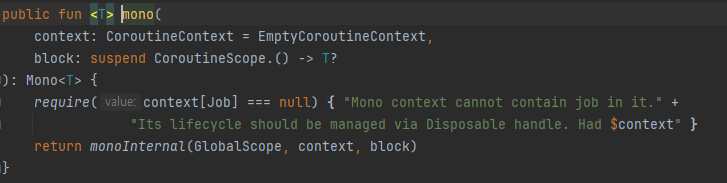
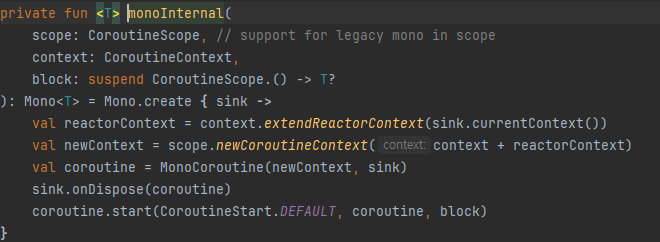
- monoInternal에서는 sink로부터 ReactorContext를 추출
- 추출한 ReactorContext로 CoroutineContext를 생성
- MonoCoroutine을 생성하고 시작
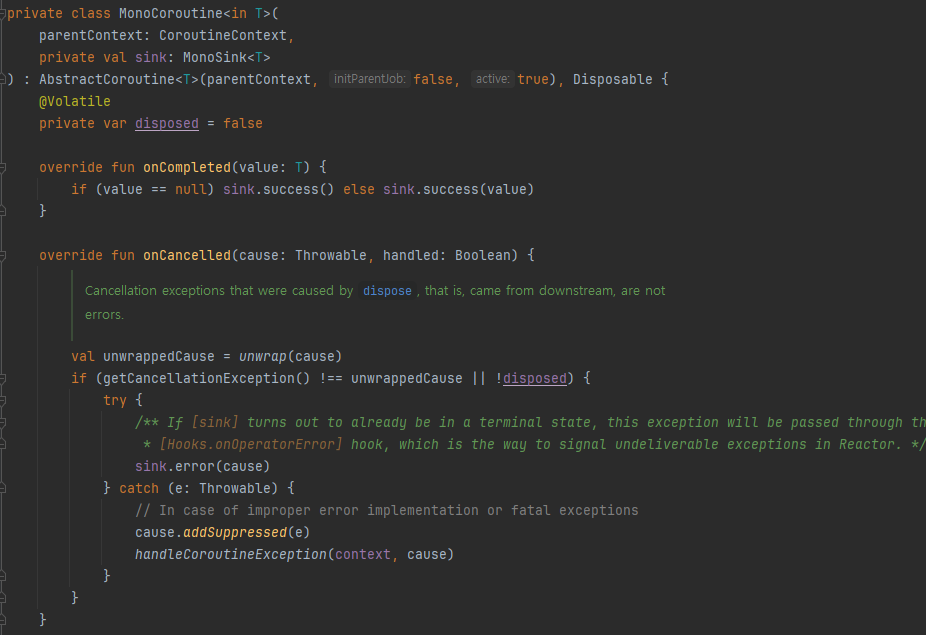
- MonoCoroutine은 sink를 인자로 받고 Coroutine이 complete 되면 sink의 success를 호출
- 반대로 cancel 된다면 sink의 error를 호출
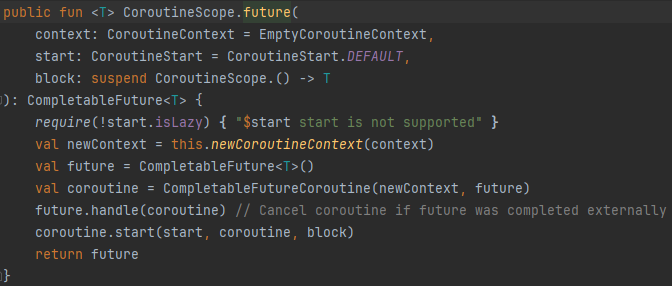
5.3 CompletableFuture를 반환하는 함수에서 suspend 함수를 호출하는 방법
- CoroutineScope를 생성하고 해당 스코프에서 Future를 실행하여 suspend 함수를 실행 후 결과를 CompletableFuture 형태로 반환
참고
패스트 캠퍼스 - Spring Webflux 완전 정복 : 코루틴부터 리액티브 MSA 프로젝트까지
반응형
'Kotlin' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Kotlin] CoroutineScope (0) | 2024.10.03 |
|---|---|
| [Kotlin] CoroutineContext (0) | 2024.10.03 |
| [Kotlin] 코루틴 (Coroutine) 개요 (0) | 2024.10.02 |
| [Kotlin] lateinit과 by lazy의 차이점 (2) | 2022.07.13 |